
The lowest possible charge indicates the most energetically favorable structure. Formal charge is calculated with the following formula:įormal charge is used to determine the best Lewis structure for a compound that has more than one choice. Lewis Structures Terminology Formal Charge: The charge on an atom in a Lewis structure, assuming all electrons are shared equally. The octet rule is a useful tool for predicting bonding in molecules especially in organic chemistry.
Hyper-coordination: Elements beyond the second row (after Neon) can have expanded octets. This rule only works for the second period (row) of the periodic table.Įlements beyond the second row can access d or f orbitals, elements are larger and have more room for bonding. The octet rule can be used to predict how atoms bond.
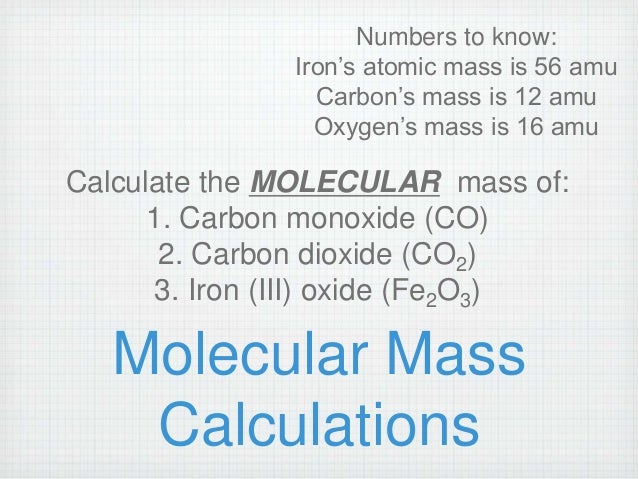
Carbon dioxide molar mass full#
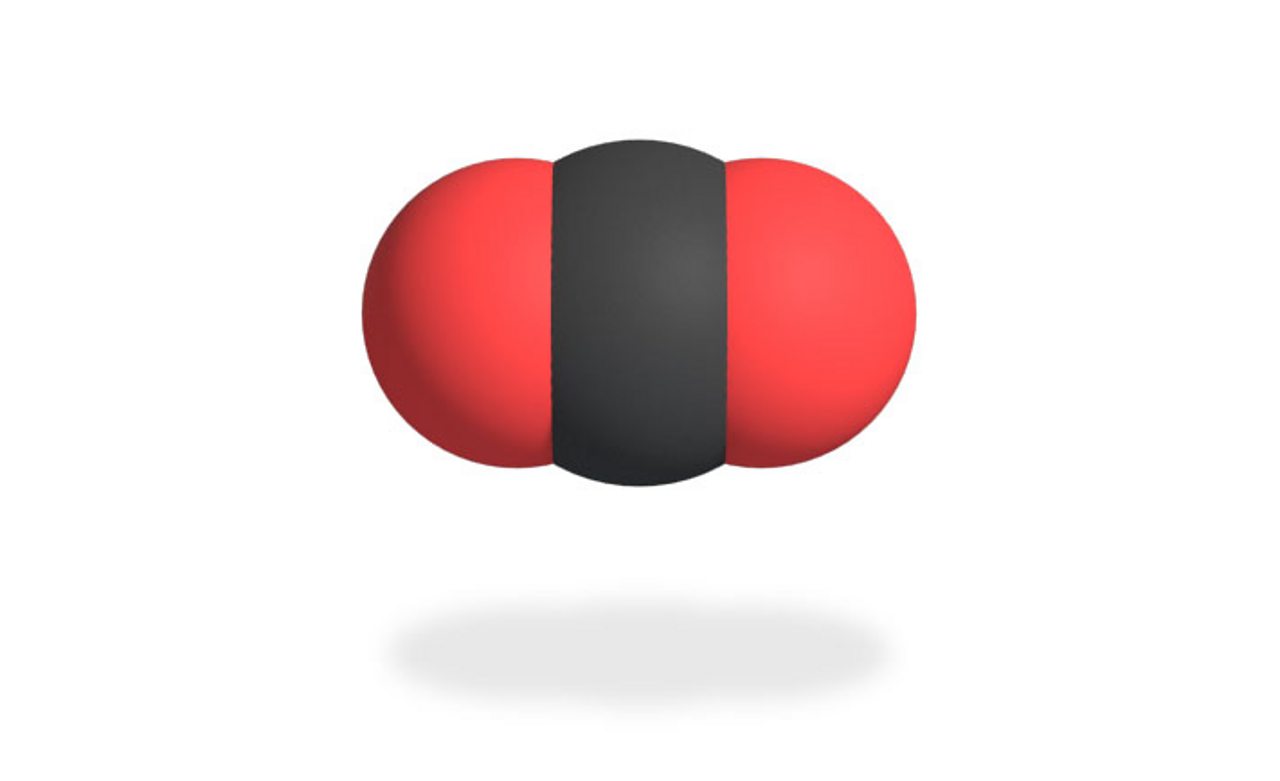
Lewis structures can be used to demonstrate bonding in molecules by showing atoms in a molecule sharing electrons to attain a full octet.Ī full outer shell containing eight electrons.Ī stable electron configuration can be attained with eight electrons in the outermost shell.īonding atoms will transfer or share electrons to satisfy the octet rule, each atom will have access to eight electrons in its outermost shell. Lewis Theory uses the octet rule to predict bonding. Representing the valence electrons of a main group element using dots surrounding the chemical symbol.Ĭhemical bonding is the attainment of a stable electron configuration through the sharing or transfer of electrons. Valence Electrons and Lewis Structures Lewis Structures: Valence electrons are responsible for the chemical properties of an atom. The valence electrons of a transition metal are located in the outermost d orbitals, as well as the outermost shell. The valence electrons of a main group element are located in the outermost shell. The number of valence electrons an element has determines the chemical properties of that element.Įlements in a column (group) have the same number of valence electrons, this is why elements in a group have similar chemistry. The valence electrons are the electrons involved in chemical bonding between atoms. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom. The charged ions are then attracted to each other due to electrostatic forces.Įlectrostatic Attraction Between Ions = Ionic Bond The metal transfers its electron(s) to the nonmetal so both elements reach the nearest noble gas configuration. When metal and nonmetal atoms approach each other an electron transfer takes place.

Metals and nonmetals want to attain the nearest noble gas configuration. Nonmetals have a tendency to gain electrons, forming anions. Metals have tendency to lose electrons, forming cations. Polar Covalent Bonding in Hydrogen Fluoride ( ) Two or more molecules or atoms of the same type.Ĭhemical Bonding Classes of Chemical Bonding IonicĮlectrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions.īonding atoms are generally metals and non-metals.Įlectron is transferred from one element to another.Įlectrons are unevenly shared between atoms. Two or more bonded atoms of different types. Two or more bonded atoms of the same type. Video Transcript Chemical Bonding Terminology


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
